Environmental pollution: effects and countermeasures
April 11, 2024 • Reading time: 16 Min

In today's world, which is characterized by global challenges, the right to a healthy environment is becoming increasingly important. Our livelihoods and the future of generations to come depend largely on an intact ecosystem. However, the reality is that pollution continues to pose a serious threat to our livelihoods. From air pollution and soil contamination to pollution of the oceans - the effects are manifold and affect us all. Especially in times of climate change and global warming, the urgency of taking action to protect our environment is becoming ever more apparent. Alarming signals in this context are, for example, the loss of biodiversity and the destruction of natural habitats, which make it clear that there is an urgent need to rethink our approach to nature. This article analyzes different types of pollution, discusses their impact on people and nature, and examines the role of climate lawsuits and other measures to enforce environmental protection measures and reduce environmental pollution.
In short: Environmental pollution at a glance
Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances into the air, water, or soil. The effects of this impact both nature and human life. Air pollution can lead to health problems, while marine and freshwater pollution threatens marine habitats and can affect drinking water quality. Soil pollution negatively affects ecosystems and reduces soil fertility.
There are different types of pollution such as air, water, and soil pollution, as well as non-material emissions such as radiation, noise, and light pollution. Industry, energy production, and intensive agriculture contribute to this.
The consequences of pollution are dramatic and affect not only wildlife but also humans. Climate lawsuits have gained importance worldwide, enabling legal action against governments and companies to protect the environment and climate.
To combat pollution, measures such as reducing single-use plastics, monitoring emissions, regulating harmful chemicals, and controlling global CO₂ emissions are necessary. A sustainable future requires global cooperation and the implementation of international agreements.
Governments enforce strict environmental standards, companies are increasingly switching to more eco-friendly practices, and consumers demand sustainable products and services. Individual actions can also make a contribution, such as reducing single-use plastics, saving energy, and consuming consciously.
It is crucial to take measures to reduce environmental impact in order to protect our health and the future of the next generations. Together, we can create a clean and healthy environment for all.
Subscribe to never miss any insights.
Receive regular insights and updates on the latest developments in the areas of LkSG, CSDDD, CSRD, ESRS, compliance, ESG and whistleblowing. Our newsletter helps you to simplify your compliance processes.
Environmental pollution: a definition
The right to a healthy environment is of crucial importance as it forms the basis for the well-being of all living beings on our planet, including us humans. An intact environment is not only important for our physical health, but also for our mental well-being.
Furthermore, the right to a healthy environment is closely linked to human rights. Everyone has the right to clean air, clean water and an intact natural environment. These rights must be protected and preserved in order to ensure a sustainable livelihood for present and future generations.
In a world where pollution and climate change are on the rise, it is more important than ever to take action to protect our environment and our health.
Pollution is a pervasive problem that has a dramatic impact on the right to a healthy environment. This right is directly linked to the obligation to protect and preserve the environment. A consistent fight against pollution is therefore essential to guarantee this right and ensure the quality of life of future generations. But what exactly is pollution?
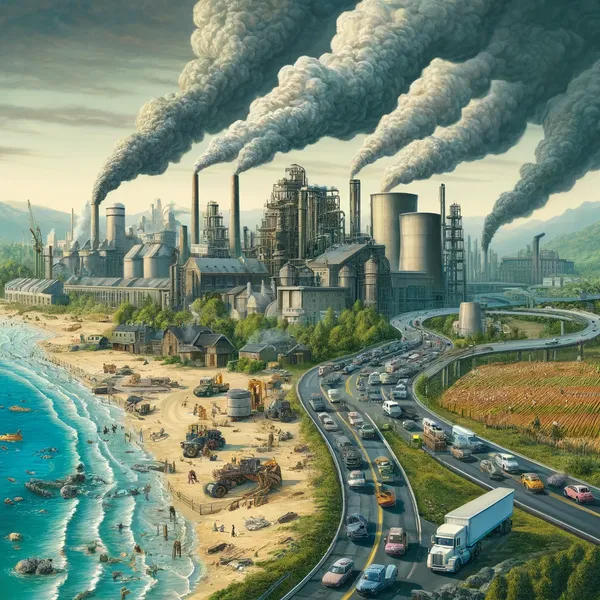
Environmental pollution is the introduction of harmful substances, such as heavy metals and pesticides, into the environment, be it air, water or soil. The effects of this are manifold and affect not only nature but also human life. Chemicals in the air can lead to health problems, while polluted water can affect not only access to drinking water but also agriculture. Air pollution from waste or emissions not only affects the climate, but also people's quality of life. Pollution is therefore a complex issue with a direct impact on our daily lives and the health of our environment.
Types of environmental pollution
Air pollution:
Air pollution is a serious environmental problem that has far-reaching effects on our health and the environment. It is mainly caused by pollutants that enter the atmosphere and lead to a deterioration in air quality. These harmful substances are associated with the development of asthma, heart disease and strokes.
One problem in combating air pollution is the constant change in harmful substances. There are numerous air pollutants that are harmful to the environment. When these pollutants are released into the air, they react with each other and with the environment in complex ways, depending on temperature, humidity and other environmental conditions.
Marine pollution:
Marine pollution involves the introduction of harmful substances such as plastic waste, oil, chemicals and wastewater into the oceans. This has serious consequences for marine ecosystems and the health of marine life. Plastic waste, especially single-use plastic such as plastic bottles, packaging and plastic bags, poses a major threat to the environment. Plastic waste, for example, can be mistaken for food by animals and lead to fatal injuries or suffocation. Oil spills also have devastating effects on marine life and can destroy entire ecosystems. Chemicals and sewage can pollute water and affect water quality, with long-term consequences for the environment.
Pollution of fresh water:
The contamination of drinking water is a significant environmental hazard that severely affects both ecosystems and human health. It includes the discharge of harmful substances such as chemicals, pesticides and sewage into rivers, lakes and groundwater sources. These contaminants can make the water unusable for drinking, agriculture and aquaculture.
Soil pollution:
Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil by harmful substances such as chemicals, heavy metals, pesticides and waste. This pollution can be of both natural and human origin and has serious consequences. The effects can range from disturbed ecosystems and infertile soils to increased susceptibility to disease and reduced crop yields.
Contaminated sites and soil degradation:
Contaminated sites are sites contaminated by human activity that pose a risk to people and the environment. These can be caused by chemicals, heavy metals or other pollutants and lead to permanent soil pollution. Soil degradation, on the other hand, refers to the loss of soil quality due to erosion, sealing or overuse. This can lead to a reduction in soil fertility, the destruction of habitats and a deterioration in water quality.
Production of waste:
What does waste have to do with environmental pollution? If waste is not disposed of properly, it can have a negative impact on the environment. Plastic waste, for example, can end up in water bodies and endanger marine habitats and marine life. In addition, the incineration of waste can release harmful emissions and contribute to air pollution.
Pollution from non-material emissions:
When discussing environmental pollution and its various forms, it is important to take a closer look at pollution caused by non-material emissions. This type of pollution includes various aspects such as radiation, noise and light pollution, which are often underestimated.
Radiation can come from various sources, for example, including electromagnetic fields from mobile phone masts or X-ray machines. Although this form of pollution is less visible than air or water pollution, for example, it can have an impact on people and the environment. Exposure to ionizing radiation carries the risk of damage to health, particularly in the area of DNA.
Noise pollution, in turn, is mainly caused by traffic, industry or construction site noise and can lead to stress, sleep disorders and other health problems. Increasing urbanization further exacerbates this problem.
Light pollution is also often underestimated, although it can have a negative impact on flora and fauna as well as human biorhythms. Night-time lighting is a major problem in cities in particular.
It is therefore important not only to pay attention to the classic forms of environmental pollution, but also to keep an eye on non-material emissions and take measures to reduce these impacts.
Harmful substances
In today's world, it is very important to be aware of the various substances that can potentially pollute the environment. The list of harmful substances is long and varied. Chemicals play an important role - whether in industry or in the household. Heavy metals such as lead, mercury and cadmium in particular can have serious consequences for people and the environment.
Oil, whether in the form of crude oil or petroleum products, is one of the main causes of environmental pollution. The inappropriate use of fertilizers such as nitrate and phosphate as well as pesticides, herbicides and fungicides in agriculture also contributes to the pollution of our environment.
Burning fossil fuels leads to the release of carbon dioxide, which has a negative impact on our climate. In addition to CO₂, nitrogen oxides, ammonia, sulphur dioxide, pharmaceuticals and antibiotics can also pollute the environment. Nitrogen oxides are mainly released by traffic and industrial processes and contribute to air pollution. Ammonia is mainly emitted by agriculture and contributes to soil and water acidification. Sulphur dioxide is mainly emitted by the combustion of fossil fuels and contributes to the formation of acid rain.
Pharmaceuticals and antibiotics often enter the environment via wastewater and can lead to problems such as antibiotic resistance in bacteria or changes in aquatic life.
Hydrocarbons such as benzene and radioactive substances pose additional risks. Exposure to these hazardous substances can have serious health effects, especially in the case of prolonged and intensive exposure.
Who causes pollution? Sources of pollution
Environmental pollution is mainly caused by various industrial sectors. Heavy industry and energy production in particular make a significant contribution. The release of pollutants and greenhouse gases pollutes the environment and contributes to climate change.
Air
The main source of air pollution is human activity. Emissions are mainly caused by the use of energy in households, industry, transportation and agricultural activities. Emissions are particularly high in the transport sector. High CO₂ emissions from vehicles and exhaust gases from the combustion of fossil fuels contribute to air pollution and have a negative impact on the quality of the air we breathe. In addition, the daily use of roads produces further pollutants through erosion. Combustion products such as nitrogen and sulphur oxides turn into acid rain in the atmosphere, which acidifies the soil. This leads to the release of aluminum ions in the soil, which damage plants and soil bacteria.
According to the European Environment Agency, domestic heating systems are a significant source of air pollution. Commercial, institutional and residential buildings contribute to 53% of particulate matter (PM2.5) emissions. Traffic accounts for around 45% of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions in Europe and a significant proportion of other major pollutant emissions. Road traffic is also the most common source of environmental noise, negatively affecting many people in Europe. In contrast, 90% of ammonia emissions in Europe are caused by agriculture.
Floor
Soil is a vital resource that is often underestimated. It serves as a source of food for plants, which in turn form the basis of our diet. Soil also stores water and regulates the climate. However, environmental pollution and intensive agriculture are increasingly jeopardizing the quality of our soil.
The causes of soil pollution are varied and often regrettable. Industrial activities, improper waste disposal, agricultural practices and mining are among them. Conventional agriculture often uses harmful farming methods that can cause long-term damage. Improper waste management and nuclear waste disposal also contribute to soil pollution. Poisoned soil plays a crucial role in dramatic bee mortality, which has a serious impact on the ecosystem.
According to the European Environment Agency, 60-75% of agricultural soils in the EU have excessive nutrient inputs. The deterioration of soil quality causes costs of over EUR 50 billion per year.
Waters
The contamination of our waters is an acute environmental problem with multiple causes. Humans are the main cause, with industries such as agriculture also contributing through both the consumption and pollution of water. The introduction of pollutants such as industrial wastewater, agricultural fertilizers, household waste, oil and other pollutants plays a decisive role here. These substances enter the groundwater either through the soil or directly into rivers, lakes and oceans and have a significant impact on water quality.
Seas
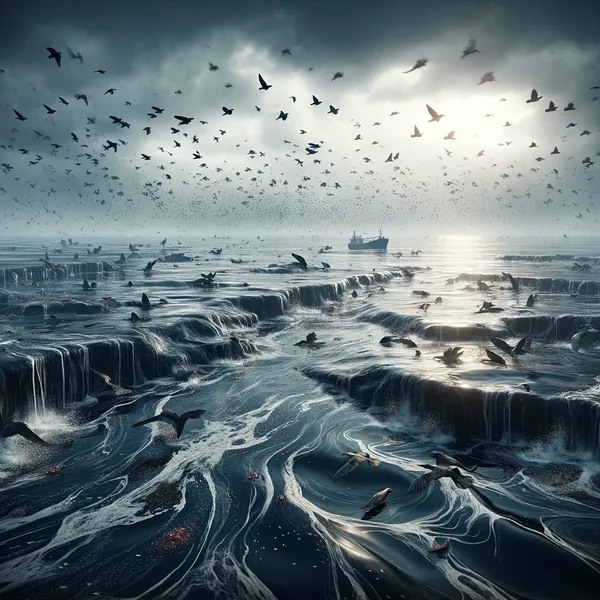
Pollution of the oceans has serious consequences for the diversity of marine life and the ecosystem. There are many different causes, ranging from plastic pollution and oil spills to chemical residues. Plastic waste poses a particularly serious threat, as it decomposes slowly and therefore remains in the sea for long periods of time.
Oil spills, on the other hand, can be caused by oil drilling accidents or tanker accidents and have devastating consequences for marine life and coastal ecosystems. This pollution not only endangers our food resources, but also threatens important fish species and seabirds. Toxic algae carpets further impair the marine habitat. Of particular concern are the so-called "dead zones", where life is no longer possible.
Overfishing of the oceans is also a decisive factor in pollution. Reckless exploitation of fish stocks destabilizes marine ecosystems and damages them in the long term.
The consequences of this environmental destruction are serious and affect not only the flora and fauna, but also coastal tourism, which suffers considerable losses.
Paying attention to sustainability as a company:
Test lawcode's CSRD tool now and create sustainability reports with ease.
The consequences of environmental pollution
Health consequences of environmental pollution
The Lancet Planetary Health study is a landmark study that takes an alarming look at the effects of environmental pollution on human health. This comprehensive analysis shows links between environmental pollution and various health problems. It shows that air and water pollution and the use of chemicals can pose serious risks to our health.
According to the Lancet study, the number of premature deaths caused by modern forms of pollution from industry, transportation and agriculture has risen by 66 percent since the turn of the millennium. Every year, more than nine million people die worldwide - meaning that pollution is responsible for one in six deaths. It is important to note that over 90 percent of these deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
The results of the study are worrying and make it clear how urgently measures need to be taken to reduce environmental pollution. It is clear that environmental protection is not only important for nature, but also crucial for our own health and the well-being of future generations.
The health consequences of environmental pollution are far-reaching. Exposure to harmful chemicals and particles in the air can increase respiratory diseases such as asthma and allergies. Similarly, polluted water can lead to gastrointestinal illnesses and other health problems. Exposure to pollution can also increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and weaken the immune system. Children, the elderly and people with pre-existing health problems are particularly at risk.
Effects on biodiversity and the ecosystem
The effects of environmental pollution on wildlife are alarming. Many animal species suffer from the consequences of polluted habitats, be it through chemical pollution of water bodies or air pollution. Endangered species in particular are often severely affected and face existential challenges. Soil and water pollution can disrupt the natural balance and endanger the animals' food sources. In addition, harmful chemicals can enter the food chain and cause long-term health problems for wildlife.
Our ecosystem is also heavily burdened by pollutants and toxins, which can lead to a significant decline in biodiversity, as many species are unable to adapt to the changing environmental conditions. For example, water pollution can lead to the destruction of aquatic habitats and a drastic decline in fish stocks. Soil pollution from chemicals is also a serious problem that affects agriculture and the life of soil organisms. Maintaining an intact ecosystem is crucial for the climate and the health of the planet.
Influence on air and water
According to a report by the European Environment Agency (EEA), air pollution killed almost half a million people in Europe in 2015 and around 6.5 million worldwide every year.
The air we breathe is of crucial importance to our health and quality of life. The release of pollutants such as chemical compounds, exhaust fumes and particulate matter into the atmosphere pollutes the air. This can lead to respiratory diseases, allergies and even serious health problems. People in urban areas, where air pollution is often particularly high, are at particular risk.
Water is essential for all living creatures on earth. However, the purity and quality of our water is being jeopardized by increasing environmental pollution, which threatens access to clean drinking water. Chemicals, waste and harmful substances find their way into our waters and pose a threat to human health and the ecosystem. According to UNICEF, thousands of children die every day due to contaminated drinking water.
The pollution of rivers, lakes and oceans also has a serious impact on flora and fauna. The importance of protecting our water resources should therefore not be underestimated.
Oil slicks and dead zones
-
Oil spills are a form of environmental pollution caused by oil leaking into bodies of water. They are often caused by accidents on oil platforms or by the transportation of oil by tankers. Oil slicks have a devastating impact on the environment as they affect water quality and pose a threat to marine life. The oil forms a thin layer on the surface of the water and can pollute or poison birds, fish and other animals. Cleaning up oil slicks is extremely difficult and costly, as special techniques and equipment are required.
-
Dead zones are areas in the world's oceans where the oxygen content decreases to such an extent that life is barely possible. These alarming zones are mainly caused by human activities such as over-fertilization and pollution of the waters. The input of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus from agriculture and wastewater causes a lot of organic matter to enter the water. These substances serve as nutrients for algae, which multiply explosively. As the algae are broken down by bacteria, oxygen is consumed, leading to a dramatic drop in oxygen levels. The effects of dead zones are devastating for marine life: fish, crabs and other creatures literally suffocate as they do not have enough oxygen to breathe. This leads to a massive extinction of species and destabilizes the fragile ecosystem of the oceans.
History of environmental pollution
The origins of environmental pollution date back to the Stone Age. There, people hunted animals and cooked them over a campfire. Ash and soot particles were the first pollutants associated with human food gathering activities, but they still polluted the environment. However, this form of pollution was still quite small.
Human settlement created new environmental pressures, such as the pollution of water and soil through livestock farming and agriculture. However, this damage was not particularly severe. As soon as people left the land and moved on, the ecosystem recovered.
The first signs that human activities can have a negative impact on the environment date back to ancient times. For example, Roman sewage led to the pollution of rivers and bodies of water.
In the 19th century, the environmental impact of industrialization reached its first peak. People abandoned nature, left their villages and moved to cities. The rural exodus that began in the 19th century marked the beginning of environmental pollution. Clouds of smoke darkened the skies above the cities and rivers were so polluted that they could no longer be used as a source of drinking water. The extent of this environmental destruction eventually led to the first environmental protection laws being passed.
Today, we are facing new challenges, particularly in connection with climate change and the increasing pressure on our ecosystems.
Can it get any worse? From pollution to environmental destruction
Pollution and environmental degradation are two terms that are often confused with each other, but have important differences. Pollution refers purely to the introduction of harmful substances into the environment, such as exhaust fumes, sewage, chemicals or plastic waste. These pollutants can contaminate the air, water and soil and endanger the health of humans, animals and plants.
In contrast, environmental degradation refers to the permanent damage or destruction of natural habitats and ecosystems. Here are some alarming cases that illustrate just how serious the impact of human activity on our environment can be:
- Oil disasters such as the Exxon Valdez tanker spill in 1989, which led to massive pollution of marine ecosystems.
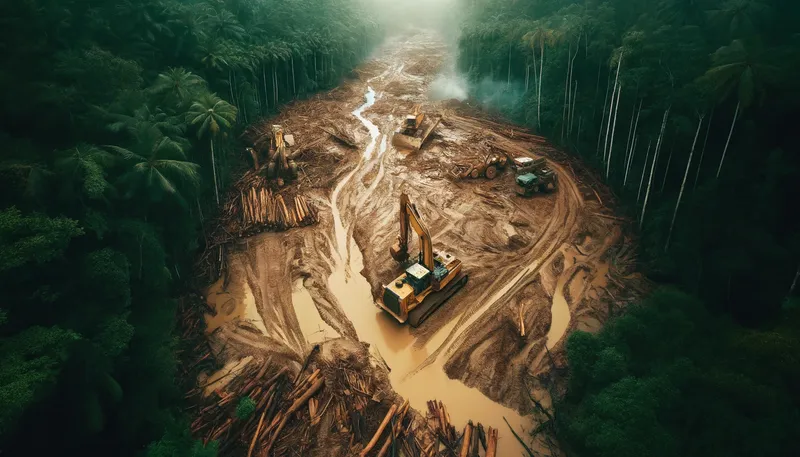
- The deforestation and slash-and-burn clearing of rainforests, for example in the Amazon region, in order to illegally gain agricultural land.
These interventions have long-term negative effects on the ecological balance and the survival of many animal and plant species.
What does environmental pollution have to do with climate change and human rights?
The link between pollution and climate change is a complex interaction that has serious implications for our planet. The constant pollution of the environment through the use of fossil fuels, deforestation and intensive agriculture leads to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, absorb the Earth's heat radiation and lead to an increase in the average global temperature - known as climate change.
Climate change leads to extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, hurricanes and heatwaves, which not only affect environmental systems but also have a massive impact on humans and animals. In addition, the warming of the oceans leads to a deterioration of the marine ecosystem and the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps, resulting in rising sea levels.
Pollution, climate change and human rights are closely linked. Environmental pollution and climate change not only threaten the natural resources of our planet, but also have a significant impact on human rights worldwide.
Increasing environmental pollution is destroying numerous habitats, endangering people's health and threatening biodiversity. As a result, many people's livelihoods are threatened and their basic human rights such as the right to clean water, food, a safe environment and an intact natural environment are not guaranteed.
Climate change exacerbates this problem by causing extreme weather events. These events often lead to massive human rights violations such as the loss of livelihoods, displacement from ancestral territories and the impairment of the right to life and health.
Climate lawsuits to strengthen environmental rights
Climate lawsuits are legal actions brought by individuals or groups against governments or companies to hold them accountable and demand action to protect the environment and climate. In recent years, climate lawsuits have become increasingly important worldwide as more and more people recognize the urgency of climate change and seek legal means to bring about change.
Such lawsuits can take various forms, including claims for damages against companies for environmental damage or lawsuits against governments for failure to implement environmental protection measures. They are often based on international environmental agreements or national laws that regulate the protection of the environment.
Climate lawsuits play a crucial role in the fight against environmental pollution. They enable those affected to take action against governments or companies that do not take sufficient measures to protect the environment. Climate lawsuits can be used to hold those responsible accountable and create pressure for change. These legal steps are an important instrument for promoting environmental protection and ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
In many countries, climate lawsuits have already led to positive changes by drawing attention to grievances and highlighting the need for action. They help to bring environmental protection issues to the forefront of public debate and raise awareness of the urgency of action. Climate lawsuits are therefore an important part of the global effort to protect the environment and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Examples of climate lawsuits worldwide
Legal action is becoming increasingly important in the global fight against climate change. Various countries are facing lawsuits aimed at holding governments and companies accountable for their role in causing environmental damage.
Climate lawsuits are currently being filed in various countries to hold governments and companies accountable and demand action against climate change. One prominent example is the constitutional complaint filed by the German environmental organization"Umwelthilfe" against the German government for inadequate climate protection measures. In the USA, citizens and organizations such as Our Children's Trust are filing lawsuits to draw attention to the violation of the right to a healthy environment. In the Netherlands, the Urgenda Foundation achieved a landmark success when the court ruled that the government is obliged to set more ambitious climate targets. These examples show that climate lawsuits are gaining importance worldwide and play an important role in the fight against climate change.
These climate lawsuits illustrate the growing awareness of the urgency of action in the fight against climate change. They also show that citizens around the world are prepared to use legal means to enforce their demands for greater sustainability and environmental protection.
Current case law of the European Court of Human Rights
The recent decision of the European Court of Human Rights has made it clear that the Court can play a decisive role in relation to the issue of environmental pollution. By applying human rights standards, the Court can play an important role in implementing environmental protection standards and protecting citizens from negative impacts on their living environment.
The Court's rulings not only set important standards, but also raise awareness of the need for environmentally friendly action in politics and business. Governments and companies are encouraged to rethink their practices and take sustainable measures to minimize negative impacts on the environment.
The recent ruling of the ECtHR has far-reaching implications for the protection of human rights, including in connection with environmental pollution. In the decision on the case Verein Klimaseniorinnen Schweiz v. Switzerland(judgment of the Grand Chamber of April 9, 2024, no. 53600/20), the Court clarified that states have a human rights obligation to protect the environmental rights of their citizens and to take responsibility for environmental damage.
Here is a compilation of the current groundbreaking case law:
The case Verein Klimaseniorinnen Schweiz v. Switzerland concerns a complaint by a Swiss association and its members, a group of older women concerned about the impact of global warming on their living conditions and health, that the Swiss authorities are not taking enough action to mitigate climate change.
In the case Verein Klimaseniorinnen Schweiz v. Switzerland, the plaintiffs complained about various failures by the Swiss authorities to mitigate climate change - in particular the effects of global warming - which they believe have a detrimental impact on their lives, living conditions and health.
They complained that the Swiss Confederation had failed to fulfill its obligations under the Convention to effectively protect life (Article 2 ECHR) and to ensure respect for their private and family life, including their home (Article 8 ECHR).
They also complained that they had no access to a court within the meaning of Article 6 of the Convention (right to a fair trial) because the state had failed to take the necessary measures to combat the negative effects of climate change.
Decision of the ECtHR
Can a human rights court rule on climate change? The ECtHR gave a clear answer: yes. Even though the Court's role is to uphold the Convention on Human Rights and its sole purpose is to protect the rights enshrined therein, it can still intervene in cases where the implementation of the Convention is affected by climate change.
First, the Court recalled the facts of climate change. It is a growing threat, and despite many rounds of negotiations and action plans, the measures taken by states still fall far short of what is needed to ensure a safe and livable planet. In view of the inadequate measures taken by states to mitigate climate change, there is an ever-increasing risk of harmful consequences for individuals, the Court stated.
The Court recognized not only that climate change is a real and progressive threat, but also that it currently has - and will have in the future - a significant negative impact on the exercise of the rights listed in the Convention. Council of Europe member states should be aware of the extreme negative impact of climate change, as evidenced by their signature of international agreements to combat climate change. They are also aware that the risks to individuals and communities will be significantly reduced if states achieve the goal of limiting the increase in global average temperatures to 1.5°C or less. In this context, a human rights court can rule on climate change.
According to the court, it is also decisive that, in addition to current generations, future generations will probably have to bear an increasingly heavy burden of the consequences of today's failures and omissions in combating climate change.
Affected rights
-
The Court found no violation under Article 2 of the European Convention on Human Rights. The Climate Seniors Association argued that the effects of climate change jeopardize the right to life and that older people are particularly affected. The Court found that it is not necessary for people to actually die for the right to life to be violated, but that a serious risk is sufficient.
An important aspect here is the concept of the margin of appreciation. This enables the Court to recognize that for many state obligations there are different legitimate measures that states can take. There may also be different views on how far a state must go to protect the law. Within the margin of appreciation, the state can choose the appropriate measures itself; outside this margin of appreciation, however, the Court would exercise stricter control.
In fact, the Court decided not to examine Switzerland's conduct in relation to Article 2, as it did not consider this necessary in view of the examination of Article 8. Although the overall judgment is positive, one might regret that the Court did not take the opportunity to clarify the link between Article 2 and climate change.
-
The Court found that Article 8 ECHR includes a right of individuals to effective protection by public authorities from the serious adverse effects of climate change on their lives, health, well-being and quality of life.
In this context, the primary responsibility of a State Party is to enact and implement laws and measures that are appropriate to mitigate the current and potentially irreversible future impacts of climate change. This obligation arises from the negative impacts of climate change on the enjoyment of rights under the Convention. With regard to Article 8 in particular, it is crucial to ensure not only the safety of the home (the actual place of family life), but also the ability to enjoy life to the full. This means that certain standards of health and well-being must be met, and if climate change jeopardizes these standards, there is a violation of Article 8.
It also emphasizes that the laws and measures must be in line with the international commitments of the member states, such as the Paris Climate Agreement and the scientific recommendations of the IPCC. Meeting these commitments requires countries to take action to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and achieve the goal of net zero emissions within the next three decades. To this end, countries must take action, set targets and timetables that are an integral part of the national legal framework and serve as a basis for mitigation measures.
What does this mean for climate change seniors? The claimants, a group of older women, many of whom have complex health needs, are particularly affected by the increasing weather extremes brought about by climate change. They argued that the inadequate measures taken by the authorities to combat climate change therefore constitute a violation of their right to respect for private and family life, including the right to health. The court agreed: according to the court, the Swiss climate law was inadequate in key respects. Firstly, it is too vague: it lacks a CO₂ budget or an equivalent, concrete mechanism to quantify and track CO₂ emission targets. There is also a lack of sufficiently defined timetables and deadlines within which a certain level of emissions reductions must be achieved. In addition, Switzerland has not always succeeded in achieving its emission reduction targets in the past. Accordingly, the court came to the conclusion that the measures taken by the Swiss government were not sufficient to adequately protect the rights of the applicants under Article 8 of the Convention. Article 8 was therefore violated.
This finding is revolutionary. Not only has the court confirmed that human rights courts have the power to deal with climate change, it has done so comprehensively. In reviewing the Swiss Climate Change Act, the court concluded that it did not meet the necessary standards to ensure the right of individuals in Switzerland to respect for private and family life. This decision highlights the need for action and makes it clear that national courts must take this new standard of review into account when they are confronted with climate cases (and they will be).
-
Before they appealed to the ECtHR, the climate seniors ' case was heard by four national courts: an administrative authority, the DETEC, and two Swiss courts. However, none of these instances assessed the merits of the case. The climate seniors therefore complained to the ECtHR that their right to access to justice and to a fair trial had been violated.
The Court agreed and found that the "essence" of the right of access to a court was impaired by the refusal of the Swiss judiciary to examine the claims of the climate seniors. It based this finding on three main grounds:
- First, the Court recalled that the right of access to justice must be "practical and effective" and not "theoretical or illusory". It is not enough for a right of access to justice to exist only on paper; an applicant must have the opportunity to have the merits of his claim examined - provided it is well-founded - and, if necessary, to obtain legal protection.
- However, the right of access to the courts is not unlimited, and states may impose restrictions, procedures and fees (among other measures) provided that they are necessary and proportionate and do not violate the "essence" of the right. In the present case, the Swiss courts set limits to restrict the actio popularis (an action in the name of the public interest) in litigation, thereby preserving the separation of powers enshrined in the Constitution. As such, the restriction pursued a legitimate aim (in the opinion of the court).
- However, the ECtHR found that the action brought by the climate seniors should not have been regarded by the Swiss judiciary as an action in actio popularis: It was a human rights complaint alleging inadequate conduct by the government. As such, the restriction was disproportionate and the core of Article 6 had been violated.
Environmental and human rights are moving ever closer together: Environmental protection is human rights protection.The recent ruling of the European Court of Human Rights in the climate seniors case makes this connection impressively clear. In the future, governments must be aware that the adequacy of their climate plans and policies will be measured against a much higher standard than before: whether they adequately protect the rights of people in their territory to health and a life in dignity.
The ruling also has significant implications for companies. Although companies cannot be brought before the ECHR, at a national level more and more courts are accepting that human rights can create "horizontal" obligations - obligations between two private parties and not just between a private party and a government. It is quite possible that the next case, Milieudefensie v Shell, will focus on human rights standards and that the ruling in Climate Senior will spill over into the private sector. Companies that want to remain at the forefront should reconsider their climate and environmental policies in light of the ECHR ruling.
Together for a clean and healthy environment: countermeasures against environmental pollution
Urgent measures to protect our habitats are needed to counteract environmental pollution. Reducing single-use plastics and promoting recycling programs are important steps to reduce water and soil pollution. Increased monitoring and control of emissions from industry and the transport sector is essential to improve air quality and protect people's health. Regulating the use of harmful chemicals in agriculture and industry is also of great importance to preserve natural habitats and protect the ecosystem. Controlling global CO₂ emissions is crucial to combat climate change and ensure a habitable climate on our planet.
Global cooperation and the implementation of international agreements are key to a sustainable future. Only together can we take effective action to curb pollution and preserve a healthy environment for future generations.
Global initiatives to combat environmental pollution
Through transnational cooperation and coordinated action, we can jointly develop effective solutions to protect the environment and bring about sustainable change. International agreements such as the Paris Climate Agreement or the implementation of the United Nations 2030 Agenda show that a global response to environmental pollution is possible.
From Kyoto to Paris: The most important milestones and initiatives in the history of environmental protection agreements
- Paris Agreement, Kyoto Protocol
- Agenda 2030 for sustainable development
- Helsinki Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes
- Marpol International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships
- Montreal Protocol on ozone-depleting substances
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and their Disposal
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
- Treaty on the Protection of Biodiversity on the High Seas (BBNJ Convention/High Seas Convention)
- Regional initiatives e.g. EU Circular Economy Action Plan
- Current: Negotiations on a global plastics agreement
Current developments in dealing with environmental pollution
In recent years, there have been significant advances and changes in the way we deal with environmental pollution. One important aspect that is becoming increasingly important is the introduction of stricter environmental regulations and standards by governments around the world. Companies are increasingly being encouraged to implement more environmentally friendly practices and find sustainable solutions for their production processes.
Another important trend is the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products and services. More and more people are attaching importance to companies acting in an environmentally conscious manner and minimizing their ecological footprint. As a result, companies are increasingly focusing on sustainability and developing innovative solutions to reduce environmental damage.
New technologies are also gaining in importance. Advances in areas such as renewable energy, waste management and water purification are helping to reduce the impact on our environment.
One current example of this is new filter technologies in factories, which help to significantly reduce harmful emissions. The principle of the circular economy is also becoming increasingly popular, as it enables companies to reduce waste and use resources more efficiently.
Another important focus is on the use of state-of-the-art technologies such as sensors and big data analyses for monitoring and early detection of environmental pollution. Through targeted data collection, potential sources of danger can be identified and preventive measures can be taken to minimize environmental damage.
These current developments show that awareness of environmental protection is growing steadily and that more and more players are actively working towards a cleaner future. It is crucial that we continue to drive this positive trend and work together to protect our environment in the long term.
Carry out simple supplier and risk analysis
Supplier management at a glance: In the lawcode Suite, you can manage all your suppliers in just one place.

What role do companies play?
Companies play a crucial role in the fight against pollution, as they have a significant influence on resource consumption and environmental impact. Compliance with environmental, social and governance(ESG) standards ensures that companies minimize their environmental impact. This obligation arises not only from legal requirements, but also from ethical standards.
There are various approaches that companies can take to reduce pollution and thus act more sustainably. Below are some compelling actions that companies can take to have a positive impact on the environment:
- Implementation of environmentally friendly production processes: An important step is the switch to sustainable production methods that reduce the consumption of resources and emissions.
- Promoting the circular economy: Switching to a circular production and consumption approach is crucial to minimizing waste and improving resource efficiency. By recycling, reusing and repairing, companies can help to extend the life cycle of their products and reduce waste.
- Use of renewable energy sources: Companies can switch to renewable energy sources such as solar energy or wind power to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Sustainable supply chains: Incorporating sustainable practices throughout the supply chain is essential. Companies should select suppliers with similar environmental standards and ensure that ethical and environmentally friendly practices are adhered to throughout the supply chain.
- Promoting environmentally conscious consumer behavior: Companies can encourage their customers to buy resource-conserving products and switch to sustainable alternatives.
- Transparent communication and reporting: Transparent communication about environmental impacts and sustainability measures is of great importance. Companies should publish regular environmental reports and provide stakeholders with insight into their efforts to reduce pollution.
- Implementation of environmentally friendly waste management: The reduction, recycling and proper disposal of waste are essential steps towards reducing the environmental impact.
- Involvement in environmental protection projects: Companies can actively participate in environmental protection programs or enter into partnerships with environmental organizations to work together on solutions to environmental problems.
By consistently pursuing these approaches and integrating them into their business strategy, companies can make a significant contribution to curbing environmental pollution and at the same time achieve long-term ecological benefits.
What can we do about pollution? 8 tips
We can take various measures to counteract environmental pollution. Here are some concrete things we can do in our everyday lives to make a positive contribution to the environment:
- Reducing single-use plastic: avoiding plastic products such as disposable bottles, bags or packaging in favor of reusable alternatives
- Promoting green transportation: It is advisable to switch to public transportation, bicycles or walking to reduce CO₂ emissions from using your own car.
- Saving energy in the home: It is advisable to switch off electrical appliances when they are not in use, use energy-saving light bulbs and invest in effective insulation for your home.
- Sustainable nutrition: It is advisable to consume regional and seasonal food, reduce meat consumption and opt for organic products in order to conserve resources.
- Waste prevention and recycling: It is important to separate waste properly in order to reduce the amount of waste through conscious consumption and the use of recyclable materials.
- Reforestation projects: It is important to promote reforestation projects in order to actively contribute to reducing CO₂.
- Conserving water: It is advisable to save water in the household, repair leaking taps and use rainwater to water plants.
- Conscious consumption: It is very important to pay attention to environmentally friendly production conditions.
It is time to stand up together for our environment and take action to keep it clean and healthy. Each of us can make a contribution, be it through conscious consumption, waste separation or supporting environmental initiatives. Only if we all work together can we curb the effects of pollution and preserve our planet for future generations.
Together against pollution
A conclusion
In summary, it can be said that the various forms of environmental pollution pose a serious threat to us and our planet. The link between pollution and climate change is complex. Environmental pollution from fossil fuels, deforestation and intensive agriculture leads to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which in turn drives climate change.
Climate lawsuits are essential in the fight against pollution and climate change. They enable those affected to take action against governments or companies that do not take sufficient measures to protect the environment. These legal actions are an important tool to bring about change and promote environmental protection. The current case law of the European Court of Human Rights also contributes to the enforcement of environmental protection standards.
It is now clear that climate change is inextricably linked to human rights and that environmental concerns are also human rights concerns. It is vital that companies and governments that violate environmental laws are aware that they could potentially face human rights consequences.
Companies play a crucial role in the fight against pollution. They have a responsibility and must reduce their environmental impact. By implementing environmentally friendly production processes, promoting the circular economy, using renewable energy sources and communicating transparently, they can have a positive impact on the environment.
As individuals, we can also take measures to counteract environmental pollution. These include reducing single-use plastic, promoting green transportation, saving energy in the home, eating sustainably, avoiding waste and recycling, supporting reforestation projects, conserving water and conscious consumption.
It is important to take measures to reduce environmental pollution in order to protect our health and the future of coming generations. Everyone has the right to clean air, clean water and an intact natural environment. An intact environment is closely linked to human rights. Environmental protection is not only important for nature, but also crucial for our own well-being.