Focus on sustainability: the importance for companies
May 3, 2024 • Reading time: 8 Min

Nowadays, sustainability is an important topic in the corporate world. But what does "sustainability" actually mean and what ideas are behind it? In this blog article, we take a closer look at what sustainability means, its basic principles and why it is so important for businesses. You will understand that longevity is more than just a trend; it is fundamental to the long-term success and good standing of businesses. From its beginnings in 18th century forestry to the important Brundtland Commission and the UN's big goals for 2030, this article focuses on how important sustainability is to our society and economy around the world. Acting sustainably is not only necessary, but also offers the opportunity to create a fairer and better future.
In brief: Focus on sustainability
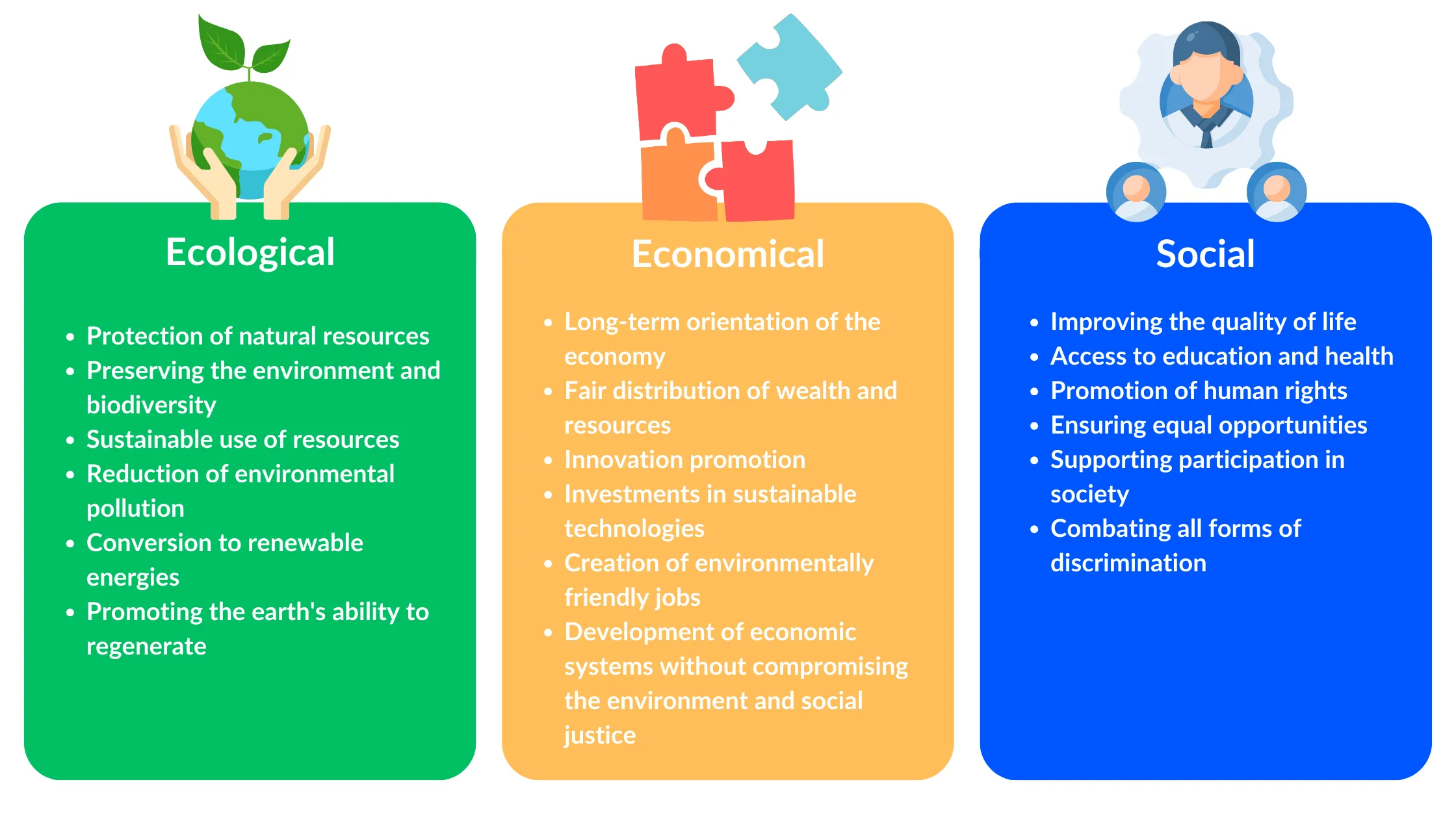
Sustainability aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This comprehensive approach considers ecological, economic, and social aspects. The concept has historical roots in 18th-century forestry and gained global significance through the Brundtland Report of 1987, which significantly influenced the idea of sustainable development. The United Nations' 2030 Agenda, with its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), provides a global framework for promoting sustainable development. These goals address environmental, economic, and social issues equally and emphasize the necessity of an integrated approach to ensure long-term and equitable development. The "Triple Bottom Line" model describes sustainability through the three pillars of environment, economy, and society. Each of these pillars is crucial: ecological sustainability emphasizes the protection and restoration of the environment. Economic sustainability promotes the fair distribution of wealth and resources through long-term economic practices. Social sustainability aims to improve the quality of life and secure human rights.
Despite its wide acceptance, there is also criticism of the three-pillar model. A common criticism is the dominance of economic interests, often at the expense of ecological and social concerns. Additionally, there is often a lack of clear implementation strategies on how to integrate the three pillars equally. In response to this criticism, alternative models such as "Strong Sustainability" and "Integrated Sustainability" have been developed. These place greater emphasis on environmental protection and stress the need to keep economic activities within planetary boundaries. Companies play a key role in implementing sustainable practices. They benefit in the long term through improved market position, higher efficiency, and a better corporate image. Sustainability in corporate management is not only necessary to secure economic success, but also to combat global issues such as climate change.
Sustainable actions in daily life are also crucial. This can be achieved through conscious decisions such as buying regional products and saving energy. Each individual can thus make a valuable contribution to sustainability.
Subscribe to never miss any insights.
Receive regular insights and updates on the latest developments in the areas of LkSG, CSDDD, CSRD, ESRS, compliance, ESG and whistleblowing. Our newsletter helps you to simplify your compliance processes.
Definition, history and global significance
Sustainability: a definition
Sustainability is an important topic that has received more and more attention in recent years, both in society and in companies. But what exactly does it mean? In short, it is about meeting the needs of the present without limiting the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The basic idea of sustainability states that we must not live today at the expense of tomorrow or consume more today than can be provided again in the future.
This idea involves the environment, the economy and society and aims to promote fair and sustainable development worldwide. The term ‘sustainability as an ethical principle’ also plays a role here: sustainability as an ethical principle encompasses far more than just ecological and economic aspects. It includes the moral responsibility to act in such a way that the needs of the present generation are met without jeopardising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This ethical responsibility requires a balance between the environment, society and the economy and demands that we view our decisions and actions from a long-term, fair and responsible perspective.
Sustainability as an ethical principle is based on six central aspects:
Firstly, we have a duty to care for future generations by preserving natural resources and the environment so that future generations can lead fulfilling lives. At the same time, it requires justice and fairness by distributing resources and opportunities equally and taking future generations into account. Another important principle is respect for nature, which recognises the environment as a valuable resource that must be protected. In addition, there is the principle of harm minimisation, which aims to reduce negative impacts on the environment and society as far as possible. Global responsibility emphasises the interdependence of all people and nations and stresses the need to act fairly and responsibly worldwide. Finally, sustainability requires long-term thinking, where decisions are not only aimed at short-term returns, but also take into account the long-term impact on the environment and society. These principles lead us to act responsibly, fairly and sustainably.
Origin of the term
The term ‘sustainability’ has a long history dating back to the 18th century. During this time, the fundamental principle of only extracting as much wood as can grow back was developed in forestry. This concept of responsible resource utilisation, which places the regenerative capacity of nature at the forefront, forms the foundation for our current understanding of sustainability. It is about living in harmony with the environment and leaving an intact natural environment and conditions worth living in for future generations. Today's challenges require a rethink in order to find sustainable solutions that are both ecologically and economically viable.
A significant turning point in the history of sustainable development was the publication of the report ‘Our Common Future’ in 1987 by the World Commission on Environment and Development, also known as the Brundtland Commission (to the report). This report defines sustainable development as the ability to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This fundamental idea has significantly influenced global discussions on environment and development and still forms the basis for numerous guidelines and strategies at international level.
Global significance of sustainability
The global relevance of sustainability is impressively illustrated by the United Nations' 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These goals, which have served as international guidelines for sustainable development since September 2015, address pressing global challenges such as poverty, hunger, climate change, inequality and environmental protection. They emphasise the inextricable link between economic progress, social cohesion and environmental responsibility.
The SDGs call on all countries, companies and individuals to make a concerted effort to promote sustainable development. The aim is to create a fairer, safer and more liveable world for all people by 2030. This shared commitment not only represents a moral responsibility, but also opens up new opportunities for innovation and growth in an increasingly resource-conscious global economy.
Three principles of sustainability
Sustainability can be divided into three areas: environment (ecological sustainability), economy (economic sustainability) and society (social sustainability). These three areas are also referred to as the three-pillar model of sustainability or the ‘triple bottom line’. This means that true sustainability can only be achieved if environmental protection, economic stability and social justice are considered together.
The three pillars of sustainability are closely interlinked and even interdependent. For example, improved environmental longevity can improve the health of the population by reducing pollution and thus contribute to social longevity. Similarly, economic progress, if made sustainable, can provide the necessary means to support environmentally friendly technologies and social programmes.
The challenge and goal is to integrate these three pillars (environmental, economic and social) in such a way that they reinforce each other and promote sustainable development that is viable in the long term. Companies and societies that recognise and implement the three-pillar model of sustainability contribute to creating a more stable, fairer and healthier world.
Below we take a closer look at the 3 different pillars of sustainability:
Ecological sustainability
Ecological sustainability requires the protection of our environment and the conservation of natural resources in order to ensure the survival of humanity and our planet. This includes not only the preservation of existing natural areas, but also the restoration of damaged ecosystems. A key point is the preservation of biodiversity, which includes all habitats and ensures that ecological balances are maintained.
Responsible use of natural resources is also of great importance. The circular economy plays a key role here by recycling and reusing materials to reduce waste. In addition, measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions must be implemented, with renewable energies such as solar and wind power playing a central role.
A sustainable environmental strategy promotes conscious consumption and emphasises effective waste management. To bring about lasting change, environmental education is essential. Only through a deeper understanding of environmentally friendly behaviour can we shape a regenerative future and leave a more liveable world for future generations.
Economic sustainability
Economic sustainability aims to make economic systems stable and fair in the long term. It promotes economic growth while taking environmental and social needs into account. Key aspects are the creation of economic resilience, sustainable business models and resource efficiency. Companies are required to invest in innovation and develop environmentally friendly technologies.
Fair access to resources and a fair distribution of wealth are also crucial. Sustainable practices, such as fair trade practices and safe working conditions, contribute to social justice and increase employee productivity. To summarise, economic sustainability secures future opportunities for generations to come through responsible economic actions.
Social sustainability
Social sustainability aims to create just and inclusive societies in which all people have access to the basic resources and rights necessary for a decent life. Equality and equal opportunities are key to ensuring that everyone - regardless of gender, origin or social status - has the same opportunities for education and work. Companies must create structures that prevent discrimination and guarantee access to education and healthcare.
Another important aspect is social justice, which deals with the fair distribution of wealth and resources. Companies should also offer secure and fair jobs in order to respect the rights of employees. Active participation in decision-making processes promotes inclusion and strengthens a sense of social belonging. Communities play a crucial role by building social networks and projects to provide support in times of crisis. The protection of human rights must also be guaranteed. Cultural sustainability helps to preserve cultural diversity.
Overall, social sustainability pursues the goal of a just society in which opportunities exist for all and human dignity is respected - a basis for stability and peace for future generations.
Criticism of the sustainability triangle
The concept of the three pillars of longevity - environment, economy and society - is an important approach to promoting sustainability. Although many people use and accept this model, there is also criticism of it. One of the main criticisms is that it is often difficult to consider the three pillars simultaneously and treat them equally.
Imbalances and dominance of the economy
Companies and countries often focus too much on making money, which can be bad for the environment and society. Their primary goal is to grow and make as much profit as possible. This can lead to them paying less attention to environmental and social issues. From time to time, companies ignore and accept environmental problems or social injustice in order to achieve the desired profits.
Lack of operationalization
Another point of criticism concerns the operationalization of the concept. Although the idea of the triple bottom line is easy to understand, its practical application often remains unclear. How exactly should decision-makers integrate the three pillars on an equal footing? How do you measure success in each pillar? Without clear guidelines and measurable indicators, implementation can remain vague and inconsistent.
Alternative models and approaches
In response to this criticism, people have developed new ideas to solve problems. For example, there is the concept of "strong sustainability". This model explains that environmental and social problems cannot simply be solved with money. It places more emphasis on protecting the environment and says that economic activities must respect the limits of our planet.
Another important concept is that of ‘integrated sustainability’. This model aims to link the three dimensions of sustainability - economic, social and ecological - more closely together. The approach emphasises the need to develop systems and political frameworks that effectively combine these objectives. This includes strategies that promote sustainable development and at the same time offer a variety of benefits. Initiatives such as green economy projects play a central role here, as they support both environmental protection and job creation at the same time.
Despite the criticism, the concept of the three pillars is still a good way to understand and deal with the complexity of sustainability. It is important to keep reviewing and improving this model. This is how we ensure that it really helps to promote sustainable development.
Sustainability starts in the supply chain
Monitor the sustainability of your entire supply chain in one tool
Sustainability in corporate management: strategies and benefits
Longevity in corporate management is not only right and good, but also important for success. More and more companies are realizing that sustainable methods are necessary in order to remain competitive in the long term. Here are a few important points on why sustainability is becoming increasingly important for companies and what they want to achieve with it.
Businesses are very important in achieving the global longevity goals outlined in the United Nations 2030 Agenda. When companies take responsibility in areas such as environmental protection, social justice and economic development, they greatly help to make the world more sustainable. This includes measures such as reducing CO₂ emissions(more on the CO₂ footprint), promoting inclusive working conditions or supporting local communities.
Long-term advantages
Implementing sustainable practices leads to numerous long-term benefits for companies:
- Improved market position: Companies that focus on longevity improve their image and become more attractive to customers, investors and other important groups.
- Increased efficiency: Sustainable operating practices, such as optimizing resource consumption and minimizing waste, lead to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Better corporate image: If a company makes a strong commitment to longevity, it can improve its reputation. This helps keep customers loyal and employees happier.
It is very important for companies to build longevity into their plans and ways of working. This means that they think about longevity in all decisions, not just in special environmental programs. They adapt their production methods, select sustainable supply chains and develop products and services that are environmentally friendly and socially responsible.
Economic success and positive influence
Incorporating longevity into the business model is not only good for the planet and society, but also helps business success. Companies that actively promote sustainability are often at the forefront of innovation, attract the best employees and discover new markets. They also become more resilient to global issues such as climate change and scarce resources.
It is important for companies today to think about the future. They do this not only to help with major global problems, but also to secure their own future. When a company applies sustainable methods correctly, it brings benefits that go beyond quick monetary gains. It lays the foundation for long-term success and helps society move forward.
12 practical tips on how to make your company sustainable
-
Sustainable manufacturing and logistics processes are crucial for companies that want to fulfil their environmental responsibility and remain competitive in the long term. The first step towards optimisation is a thorough analysis of the entire value chain - from raw material procurement to delivery. Only by understanding existing resources can targeted measures be taken to reduce environmental impact.
A key aspect of sustainable processes is the promotion of resource conservation and energy efficiency. The use of renewable energies and efficient technologies makes a significant contribution to minimising the ecological footprint. It is also advisable to use resource-conserving materials in order to reduce environmental impact and maintain product quality. It is also important to ensure transparency within the supply chain. With the help of digital technologies and comprehensive data analyses, companies gain insight into the status of their resources and partners, which improves risk management and promotes trust-based collaboration.
-
The transition to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind energy not only enables companies to significantly reduce their CO2 emissions, but also supports the development of a sustainable and responsible corporate profile. Switching to green electricity and environmentally friendly heating systems is generally easy to realise and offers a cost-effective solution. These forms of energy are more environmentally friendly and sustainable compared to fossil fuels or nuclear energy.
In addition, companies have the opportunity to significantly reduce their energy consumption through targeted measures. The introduction of digital radiator thermostats, the definition of clear behavioural guidelines and the use of motion detectors are effective approaches to increasing efficiency. Energy consumption can also be optimised in business travel by promoting digital meetings and the use of bicycles, public transport or electric cars. With these measures, companies are actively contributing to achieving their sustainability goals and promoting a positive working environment at the same time.
-
The use of sustainable business accounts with environmentally conscious banks, which combine economic efficiency with ecological responsibility, can also have a positive impact on corporate sustainability. When choosing a sustainable bank, financial solutions are selected that actively contribute to creating an environmentally friendly future. Many banks invest in environmentally damaging sectors or even in the defence industry. But there are alternatives: ethical banks such as GLS Bank, Triodos Bank, EthikBank and UmweltBank conduct their business in an ecological and fair manner.
-
In order to make significant progress in the area of sustainability, a committed team is of great importance. This includes creating a corporate culture that actively supports the topic of sustainability. For example, a sustainability day can be organised or employee volunteering can be encouraged. It is a good idea to provide bicycles for business purposes, subsidise the use of public transport with job tickets and offer incentives such as Fairtrade coffee or healthy snacks.
Sustainability can be integrated as an integral part of the corporate culture and measures taken can be communicated openly and transparently. Employees could be encouraged to develop new ideas and environmentally conscious behaviour could be rewarded. Environmental protection can be promoted through the use of fuel-efficient company vehicles or electromobility, sustainable team events and individual rewards for environmentally friendly behaviour. Every step contributes to improvement and demonstrates a genuine commitment to a sustainable future.
-
Working from home has many advantages, including reduced energy consumption and costs as there is no need to travel to the workplace. Smart radiator thermostats can be implemented to make effective use of unused office space, while co-working spaces are a flexible solution for optimising the use of offices. A hybrid working model with varying home office days also supports the balance between work and private life.
In addition, companies benefit from less commuting and business travel both during and after the coronavirus crisis, which has a positive impact on the environment. According to one study, a virtual video conference with 166 participants generates around 69 kilograms of CO2, while a physical meeting emits around 52 tonnes. A study by the Institute for Applied Work Science shows that up to 850,000 tonnes of CO2 could be saved by just ten percent of the working population in Germany working from home every week. Before travelling on business, it should always be checked whether a digital meeting is sufficient; if travelling is unavoidable, it is advisable to choose public transport.
-
A paperless digital office without filing cabinets not only offers a high level of convenience, but also promotes sustainability. Care should be taken to ensure that documents are only printed out when really necessary. Modern and environmentally conscious equipment can help with this. Older devices are often less energy efficient than newer models. In terms of social responsibility, it is also important to pay attention to ergonomic furniture and retreats for employees.
-
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) means that companies voluntarily assume responsibility for society. This includes fair working conditions, particularly in an international context and across the entire production and supply chain. It also includes own initiatives, such as donations to charitable organisations, involvement in local associations or support for countries in the Global South. The aim is to reflect on the impact of one's own economic activities on society and to actively campaign for issues that are particularly important to one personally.
-
Companies can offset unavoidable CO2 emissions from travelling or production processes by providing financial support for climate protection projects. Certificates can be purchased to certify the offset. It is important to look out for reputable providers: The Federal Environment Agency offers criteria for assessing the quality of offsetting offers and recommends the ‘Gold’ standard to avoid greenwashing. One in four small companies (20 to 99 employees) and 40 per cent of large companies (over 500 employees) already offset their emissions voluntarily.
-
Environmentally friendly packaging is another important part of sustainable business strategies. Choosing materials that are biodegradable or recyclable not only helps to reduce waste, but also improves the corporate image. Companies should focus on innovative packaging solutions that minimise their environmental footprint. In addition, working with suppliers that offer sustainable materials can be an effective way to make the entire supply chain more environmentally friendly. Open communication about environmentally friendly practices and packaging alternatives to customers builds trust and encourages them to make conscious purchasing decisions as well. In combination with a comprehensive sustainability concept, this can make a significant contribution to achieving the company's overall goals in the area of environmental responsibility.
-
Sustainability should be taken into account when selecting suppliers and when making purchases and placing orders for the company. It is a good idea to source office materials from environmentally conscious suppliers and to pay attention to where the products come from and what transport routes they have travelled. Printing contracts should be awarded to companies that print on recycled paper, and hard-wearing and durable materials should be used instead of buying inexpensive but constantly new products. Fair trade coffee for the coffee kitchen, environmentally friendly cleaning products, water filters and reduced paper consumption are further measures to promote sustainability. There are no limits to creativity when it comes to sustainable practices.
-
Sustainability as well as environmental and climate protection should be actively pursued in a company, not just for competitive reasons or to improve its image. However, this does not exclude the need to communicate this commitment. It is advisable to keep the topic of sustainability present on the website and to create a special section in which measures already implemented and future goals are presented. Openness about existing opportunities for improvement and planned measures promotes transparency and credibility. Concrete measures, ideally also taken together with the team, can be shared via social media channels to inspire others to join in. Information that is important to customers, such as the environmentally friendly shipping of products, can be listed in the FAQ.
-
Companies can make significant progress in the areas of waste management, sustainable supply chains, and water consumption through targeted measures. On one hand, optimizing waste management can be achieved by implementing recycling programs and waste reduction strategies. This includes training employees on waste separation and collaborating with partners who offer innovative recycling solutions.
On the other hand, companies can promote a sustainable supply chain by setting stricter criteria for their suppliers and regularly reviewing them. By using supply chain management tools, companies can ensure compliance with ESG criteria and maintain transparency throughout the entire supply chain.
Finally, reducing water consumption is an important aspect of sustainability strategy. Companies can significantly lower their water usage by employing water-efficient technologies, as well as through the reuse and recycling of water. Additionally, awareness programs for employees that promote responsible water usage can make a decisive contribution to conserving resources.
Our contribution to a sustainable future
A conclusion
Sustainability is more than just a trend or a series of environmental actions - it is an important principle that should influence the way we live, work and interact with each other. The previous parts have shown how important and wide-ranging longevity is. It is important for major UN goals and also for everyday life in companies.
We are facing major challenges such as climate change, global inequality and the need for sustainable economic growth. These issues can seem huge, but each of us can make a difference through conscious choices. CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) initiatives by companies are crucial to promote the principles of sustainability and ensure that economic activities do not negatively impact the environment and society. Whether you are a consumer, employee, business owner or simply a citizen, every action matters.
Implementing sustainability in everyday life is easier than you might think. When shopping, for example, you can look for products from the region and choose seasonal foods to avoid long transportation routes and thus CO₂ emissions. Using public transport or cycling instead of driving your own car also helps to reduce the environmental impact. At home, you can save energy by using LED lamps and not leaving appliances on standby unnecessarily. Recycling waste and avoiding plastic packaging also helps to conserve resources and protect the environment. By following these simple steps, each of us can contribute to a more sustainable world.
Longevity is crucial for the future of future generations, as it creates the basis for an environment worth living in. By using resources responsibly, minimizing CO₂ emissions and protecting biodiversity, we ensure that future generations inherit a world that is not only habitable but also prosperous. "Weak sustainability" assumes that natural resources can be replaced by man-made capital as long as the total value of the capital stock is preserved. Sustainable companies play a crucial role in this by integrating environmental and social responsibility into their business strategies and thus becoming role models for other companies and society. Acting sustainably means caring for the earth so that our children and grandchildren can enjoy the same natural resources, clean air and pure water that we do. Without sustainable practices, we risk irreversible damage to our planet, which could lead to resource scarcity, deteriorating health and a diminished quality of life for all future inhabitants. Therefore, it is important that we take responsibility now and prioritize longevity in our daily decisions.
So let's use the ideas and insights from this article to actively promote sustainable practices and contribute to a better world. The path to longevity means constant learning, adapting and improving. We must walk this path together, with the clear goal of creating a better and fairer world for the future. When we act today, we lay the foundation for tomorrow. So, let's walk this path with determination and hope.